What Causes Ovarian Cysts?
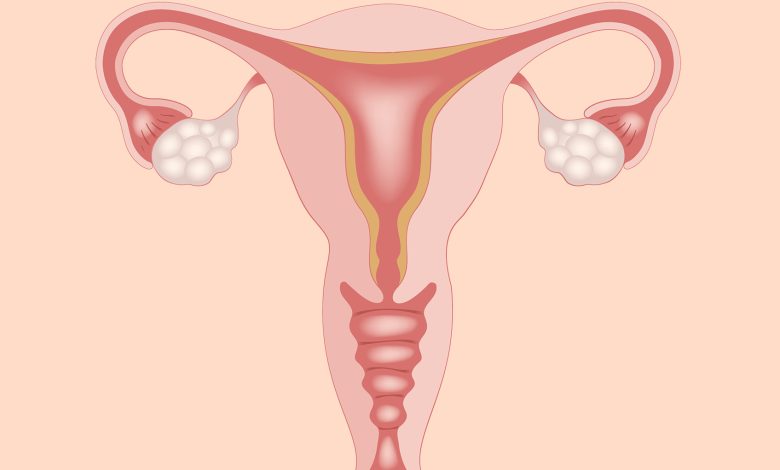
The female reproductive system includes the ovaries. They’re on both sides of the uterus in the lower abdomen. Women have two ovaries, which produce eggs, as well as estrogen and progesterone hormones. On one of the ovaries, a cyst might form, which is a fluid-filled sac. Throughout their lives, many women will acquire at least one cyst. Cysts are usually painless and have no symptoms. This blog will help you understand causes and Ovarian cysts treatment.
Ovarian Cysts Are Caused By A Variety Of Factors
Your ovaries generate little cyst-like structures called follicles in the early stages of every menstrual cycle; when ovulate, egg is released from one of these follicles. A ‘functional cyst’ develops when a normal follicle continues to expand. Within two or three cycles, this sort of cyst normally vanishes.
Hormone changes (including fertility medicines), pregnancy, endometriosis, and a serious pelvic infection that travels to your ovaries are all risk factors that need Ovarian cysts treatment.
Ovarian Cysts Come In A Variety Of Shapes And Sizes
Ovarian cysts come in a variety of shapes and sizes. Functional cysts, on the other hand, are the most prevalent form. Follicle and corpus luteum cysts are the two forms of functional cysts.
Cyst Of The Follicle
An egg matures in a sac called a follicle during a woman’s menstrual cycle. This sac can be seen within the ovaries. This follicle or sac usually bursts open and releases an egg. The fluid inside the follicle might develop a cyst on the ovary if the follicle does not burst open.
Ovarian Cysts Are Caused By A Variety Of Factors
Your ovaries generate little cyst-like structures called follicles in the early stages of every menstrual cycle; when you ovulate, an egg is released from one of these follicles. A ‘functional cyst’ develops when a normal follicle continues to expand. Within two or three cycles, this sort of cyst normally vanishes. Hormone changes (including fertility medicines), pregnancy, endometriosis, and a serious pelvic infection that travels to your ovaries are all risk factors for ovarian cysts.
Cysts In The Corpus Luteum
Follicle sacs usually disintegrate once an egg is released. Ovarian cysts can also be classified as:
- Hair, fat, and other tissue can be found in dermoid cysts, which are sac-like growths on the ovaries.
- Cystadenomas are noncancerous growths that can develop on the ovaries’ outer surface.
The Signs And Symptoms Of An Ovarian Cyst
Ovarian cysts frequently do not create any symptoms.
- bloating or swelling in the abdomen
- bowel motions that hurt
- pelvic discomfort before to or during menstruation
- soreness in the lower back or thighs during the intercourse
- soreness in the breasts
- vomiting and nausea
Complications Of Ovarian Cysts
The majority of ovarian cysts are benign and disappear on their own without therapy. There are few, if any, symptoms associated with these cysts. A malignant cystic ovarian tumor may be discovered during a normal checkup in a small percentage of cases.
Ovarian torsion is another uncommon ovarian cyst consequence. An ovary twists or moves from its original position as a result of a big cyst. The ovary’s blood supply is cut off, and if not treated, the ovarian tissue might be damaged or die. Ovarian torsion accounts for roughly 3% of emergency gynecologic procedures, despite its rarity.
An Ovarian Cyst Can Be Diagnosed In A Variety Of Ways
During a normal pelvic examination, your Gynecologist in Kolkata might notice an ovarian cyst. They may order an ultrasound to confirm the cyst’s presence if they see swelling on one of your ovaries. Ultrasound (ultrasonography) is a diagnostic imaging process that creates an image of your inside organs using high-frequency sound waves. Ultrasound can be used to determine the size, location, shape, and content of a cyst (solid or fluid filled).
Ovarian cysts treatment is detected using the following imaging techniques:
- A CT scan is a sort of body imaging that produces cross-sectional images of the organs inside the body.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a technique that uses magnetic fields to provide detailed images of organs within the body.
- An ultrasound device is a type of imaging instrument that is used to see the ovary.
An Ovarian Cyst Can Be Treated In A Variety Of Ways
If the cyst does not go away on its own or develops larger, your Gynecologist may prescribe therapy for Ovarian cysts treatment.
Pills for contraception
Oral contraceptives can also help to reduce the risk of ovarian cancer. Postmenopausal women are more likely to get ovarian cancer.
Laparoscopy
If the cyst is small, your Gynecologist can do a laparoscopy to surgically remove it and use the findings of an imaging test to rule out cancer. Your Gynecologist will make a small incision around your navel and then remove the tumor with a little instrument inserted into your abdomen.
Laparotomy
If you have a huge cyst, your Gynecologist can surgically remove it from your belly through a major incision. They’ll do an urgent biopsy, and if the cyst is found to be benign, they’ll proceed.
What Are The Long-Term Prospects?
Premenopausal women with ovarian cysts have a fair prognosis. The majority of cysts dissolve after a few months. Recurrent ovarian cysts, on the other hand, can arise in premenopausal women and women who have hormone abnormalities.
Some cysts might reduce fertility if left untreated. Endometriosis and polycystic ovarian syndrome are both known to cause this. Your Gynecologist can remove or reduce the cyst to boost your fertility. Fertility is unaffected by functional cysts, cystadenomas, and dermoid cysts.
Conclusion
Some ovarian cysts are linked to lower fertility, whereas others aren’t. Endometriosis and cysts caused by polycystic ovarian syndrome might make it difficult for a woman to conceive. Functional cysts, dermoid cysts, and cyst adenomas, on the other hand, are not linked to infertility unless they are enormous. If your Gynecologist in Kolkata detects an ovarian cyst while you’re pregnant, the therapy will be determined by the cyst’s kind and size. The majority of cysts are benign and do not require surgery. However, if the cyst is cancerous or ruptures or twists (known as torsion), or if it is too big, surgery may be required.
Also Read –
How to strengthen your body after miscarriage?
Is normal delivery possible with low amniotic fluid?
Treatment options for infertility in women at Cloudnine Hospital



