what is UV printing? Its Complete Working in Detail
Definition: what is UV printing?
UV printing is not to be understood as a printing process in the narrower sense that differs from others due to its printing method. Rather, UV technology can be used in various processes such as offset, flexographic or digital printing. It enables particularly fast drying, more precisely: a sudden hardening of the printing inks. This results in two basic benefits of UV printing:
- The rapid curing of the ink under UV light enables immediate print processing.
- UV inks do not penetrate the substrate: This is why both paper and non-absorbent substrates can be print on.
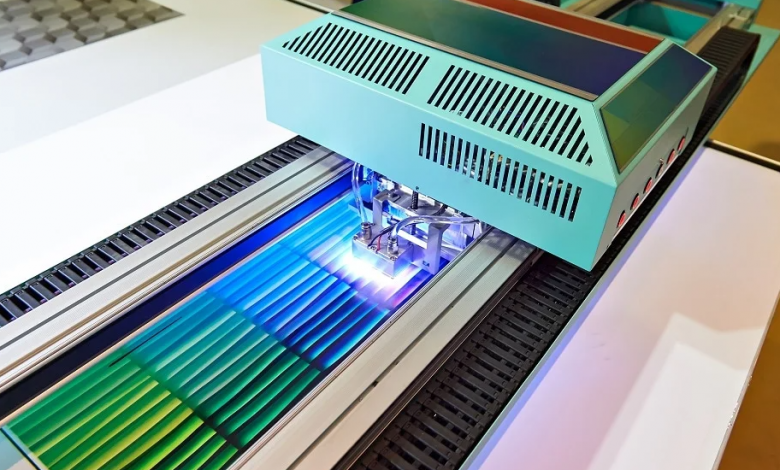
How does UV printing work?
The way printing works is base on the use of inks, printing inks and varnishes that cure under light. As a result of this reaction, the colors cure suddenly without penetrating the substrate.
Photoinitiators are photoactive substances contain in inks, paints and varnishes. When expose to radiation, they form radicals (reactive atoms or molecules) and cause the polymerisation of color components such as B. unsaturate acrylates. The UV inks do not contain any solvents or thinners and are therefore consider to be user-friendly and environmentally friendly.
Video: The principle of conventional UV curing
The following video from IST METZ, manufacturer of UV systems, explains the principle of drying and curing printing inks, varnishes and primers using ultraviolet light. The system consists of three components:
- UV lamps
- Reflectors
- Ballasts
As a result, the discharge arc is constrict and the current density increases. When the plasma has reach a sufficiently high temperature, the excitation of the mercury atoms causes UV radiation to be emit. Some of the radiation hits the substrate directly, and some of it is direct onto it by the reflectors.
Light-emitting diodes are increasingly being use instead of mercury vapor lamps.
Advantages and disadvantages of LED UV printing
With LED-UV printing, the colors etc. are irradiate by light-emitting diodes in LED light sources. Compare to conventional curing with mercury vapor lamps, LEDs offer some advantages, but also disadvantages. The following overview summarizes them.
| Advantages of LED UV printing | Disadvantages of LED UV printing |
|
|
Another thing to consider: LEDs do not emit a light spectrum like mercury vapor lamps, but monochromatic light in a narrow bandwidth. For complete curing, the ink, substrate and curing system must be precisely matched to one another. If the UV ink does not fully cure, there is a risk to health.
In which printing applications is UV technology used?
The printing processes in which the technology is used are just as diverse as the products from printing. These include the following five procedures, which are presented in the next few paragraphs:
- Tin printing
- Label printing
- Digital printing
- Flexographic printing
- Offset (roll and sheet)
UV metal printing
In UV sheet metal printing, sheet steel and aluminum are printed, which are processed into cans or boxes, bottle lids or screw caps. For these, as for all other mass-produced products, printing is suitable due to its constant quality, low energy consumption and speed.
Digital UV printing
Digital printing is characterized by its photo-realistic quality: Since the size of the ink droplets can be regulated individually, even very fine lines can be displayed very sharply. In addition to paper and cardboard, very different materials and surfaces can be printed:
- Acrylic glass and glass
- wood
- Ceramics and tiles
- Plastics, e.g. B. Signs, PVC foam panels
- Marketing items such as pens, mouse pads
UV label printing
UV technology is suitable for label printing, for example, because its products are very resistant to mechanical stress (high scratch and abrasion resistance) and to chemicals. Here is an overview of the substrates and applications:
| Substrates | Applications |
|
|
UV flexographic printing
In flexographic printing, packaging is primarily designed. They consist of film or foil, cardboard or cardboard, aluminum and laminate.
UV offset
So-called UV offset is a special form of offset printing. This process variant requires special equipment for the offset printing machines and special aids (UV-reactive printing inks and UV lamps). Both the roll and the sheet are printed. The following table provides an overview of the various areas of application and substrates for UV web offset and UV sheetfed offset:
| UV sheet-fed offset | UV web offset | |
| Substrates |
|
|
| Applications |
|
|
Materials for UV printing
The consumables for printing – for example inks and varnishes – differ depending on which technology is used for curing. inks and inks for LED, for example, are generally somewhat more expensive than for systems with conventional curing. But what about the properties in terms of quality and development? Drucker carried out a survey of the following manufacturers of printing inks :
- Epple AG
- Flint Group
- Jänecke + snowman
- Marabu GmbH & Co. KG
- Siegwerk
- Sun Chemical
- Zeller + Gmelin
In addition to the USPs, potential areas of application for the inks were also in demand. The results of the survey are detailed in the e-dossier “Printing inks for LED drying”.
Finishing with UV varnish
UV varnish is one of the most important types of varnish. Compared to other paints, it can be applied inline in very thick layers. The resulting lacquer film can usually no longer be distinguished from foil lamination. Due to their high thickness, the UV lacquers also achieve gloss values that are difficult to achieve with water-based lacquers.
Working world UV printing
Printing with technology is one of the more recent processes in a printing industry that has a long history and is currently undergoing major changes. The changed media usage behavior – away from print and towards online – is favoring trends such as increased industrialization and cross-media production.



