The process of representing a number as a product of its prime components is known as prime factorization. A prime number is one with precisely two components, one and the value of the number itself. Let’s look at the number 30 as an example. Although we know that 30 equals 5, 6, 6 is not a prime number. Because 3 and 2 are prime integers, the number 6 is written as 2 x 3. As a result, the prime factorization of 30 is 2 x 3 x 5.
Throughout this article, you will discover how to use prime factorization to solve a variety of mathematical problems, which will be accompanied by solved examples.
Definition Of Prime Factorization
Prime factorization is the technique of expressing a number as the product of prime numbers. Prime numbers are those that have only two factors, one, and the number itself, such as 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, and so on.
The term “prime factorization” refers to the process of representing a quantity as a result of multiplication of two numbers. The prime factorization of number 40 will be 2 x 2 x 2 x 5.
What are Factors and Prime Factors?
Prime factorization is the process of factoring a number while only considering the prime numbers (2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, and so on) among all the factors. The prime factors are the numbers that totally divide the original number and cannot be divided into other factors.
A number’s factors are the numbers that are compounded to produce the original value. For example, 4 and 5 are factors of 20, i.e. 4 x 5 = 20, whereas prime factors of a number include prime integers multiplied to obtain the original number. For example, the prime factors of 20 are 2, 2, and 5, i.e. 2 x 2 x 5 = 20.
Methods To Find Prime Factorization
There are several techniques for determining a number’s prime factorization. The following are the most frequent methods for determining prime factorization:
- Prime factorization using factor tree method
- Division method of prime factorization
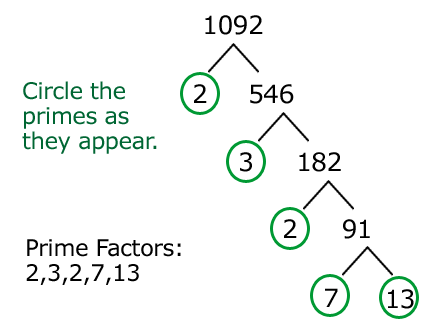
How To Find Prime Factors Using Factor Tree Method
The factor tree technique finds a number’s factors, which are then factored further until we reach the prime numbers. Follow the steps below to evaluate a number’s prime factorization using the factor tree method:
- Step 1: Think of the number as the tree’s root at the top of the factor tree.
- Step 2: Next, as the tree’s branches, put down the matching pair of components.
- Step 3: Parameterize the composite factors discovered in step 2, then note down the set of components as the tree’s next branch.
- Step 4: Repeat the same procedure till you have all of the composite factors’ prime factors.
How To Find Prime Factors Using the Division Method Of Prime Factorization?
By dividing the number by prime numbers, the division method may also be used to discover the prime factors of a big number. To get the prime factors of an integer using the division technique, follow the steps below:
- Step 1: Dividing the total number by the lowest prime number in such a way that the smallest prime number entirely divides the value.
- Step 2: Reduce the division of step 1 by the lowest prime integer once again.
- Step 3: Repeat the above procedure until the quotient is equal to one.
- Step 4: Lastly, combine all of the prime factors that are division decimal digits.
Conclusion
The above article talks about the prime factorization and the various numbers that lead to prime factors at some point or the other. For more details students can refer to Cuemath, an online platform that will let them know in detail about the entire concept along with the ways to find the greatest common factor with the help of prime factorization.



